Ultraviolet (UV) light, an invisible form of electromagnetic radiation, plays a crucial role in various applications, from scientific research to everyday uses. This article explores the nature of UV light, its different types, and how it interacts with materials, making it a valuable tool across diverse fields.
What is UV Light?
Ultraviolet (UV) light is a form of electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than that of visible light but longer than X-rays, ranging from about 10 to 400 nanometers. It is invisible to the human eye, although some people may be able to perceive light at shorter wavelengths under certain conditions. The UV spectrum is further divided into different subtypes, including UVA (315–400 nm), UVB (280–315 nm), and UVC (100–280 nm), with vacuum or extreme UV having wavelengths from 10 nm to 180 nm.
Types of UV Radiation: 3 Types of UV Radiation and Their Effects
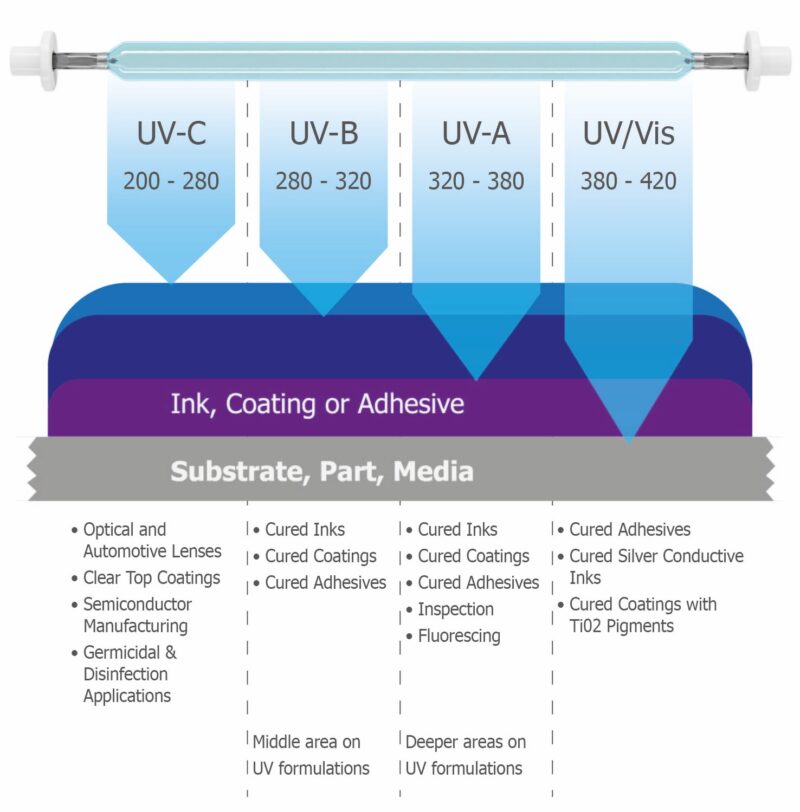
UV radiation is broadly classified into different bands based on wavelength. There are 3 types of UV radiation as following:
Shortwave UV (UV-C): Primarily produced by low-pressure mercury arc lamps, shortwave UV has a wavelength of approximately 254 nanometers (nm). This specific wavelength is highly effective for germicidal applications, as it disrupts the DNA of microorganisms.
Meddiumwave UV (UV-B) (280–315 nm) It has higher energy compared to UVA light but lower energy than UVC light. This intermediate energy level makes it capable of causing significant effects on biological systems, widely used for skin disease treatment, Vitamin D Synthesis, Plant growth regulation....
Longwave UV (UV-A): Generated by low- to high-pressure mercury arc lamps, longwave UV has wavelengths ranging from 320 to 400 nm. Often referred to as "black light," it's used for various applications, including fluorescence analysis and curing certain materials. for example the 365nm uv lamp is widely used for Drying of Inks and Coatings
(Note: A nanometer (nm) is a unit of length used to measure wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum, equal to one billionth of a meter.)
Safety Precautions:
While longwave UV (UV-A) and UV-B are generally considered safe for casual exposure, shortwave UV (UV-C) can be harmful. Direct exposure to shortwave UV can cause skin burns and eye irritation. Therefore, it's crucial to control exposure and wear appropriate personal protective equipment, such as UV safety goggles, when working with shortwave UV sources.
Typical Applications of UV Light By Their Clasifications
Applications of UV-A:
Medical field: Used for treating some skin diseases such as psoriasis and vitiligo. It can also be used in photochemotherapy and combined with specific drugs to enhance the treatment effect.
Beauty industry: Commonly found in tanning beds. By emitting UV-A rays, it stimulates the skin to produce melanin and darken the skin to achieve a tanned effect.
Industrial field: Can be used to cure certain adhesives, inks, and coatings, improving production efficiency and product quality. It is widely used in industries such as printing and electronics.
Detection field: Used as a black light to make many substances produce fluorescence or phosphorescence, facilitating detection and identification. For example, it is used in forensic science to detect traces such as fingerprints and body fluids, and to identify the authenticity of currency and artworks. It can also be used in HVAC systems to detect leaks in air conditioning systems.
Agricultural field: Has a strong attraction to insects and can be used to make insect traps to attract and capture pests and reduce damage to crops.
Applications of UV-B:
Medical field: It is an important means for treating various skin diseases. For example, narrow-spectrum UV-B can be used to treat psoriasis, eczema, vitiligo, etc. By regulating the skin immune system, it promotes the normal growth and differentiation of skin cells and alleviates symptoms.
Health care: Moderate exposure can promote the synthesis of vitamin D in human skin, which is helpful for calcium absorption and bone development.
Agriculture and horticulture field: In indoor horticulture and greenhouse cultivation, it can promote the growth and development of plants, improve the immunity of plants, enhance their resistance to pests and diseases, and also improve the quality and color of fruits and increase the nutritional value of agricultural products.
Animal breeding field: It is crucial for the breeding of pets such as reptiles. It helps them synthesize vitamin D3 and maintain normal calcium metabolism and bone health.
Astronomical observation field: Observation in the ultraviolet band can provide information such as the temperature, chemical composition, and magnetic field of celestial bodies, helping astronomers understand the evolution of the universe and the physical properties of celestial bodies more deeply.
Applications of UV-C:
Disinfection and sterilization field: It has strong sterilization ability and can destroy the DNA or RNA structure of microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi, making them lose activity. It is widely used for air, water, and surface disinfection in places such as hospitals, laboratories, food processing plants, and pharmaceutical factories. For example, it is used for disinfection and sterilization of hospital operating rooms, wards, and medical devices, environmental disinfection of food processing workshops, and purification treatment of drinking water and swimming pool water.
Environmental protection field: Can be used to treat industrial waste water and waste gas, degrade organic pollutants in them, and decompose them into harmless substances to reduce environmental pollution. - Daily life field: Some household air purifiers, water dispensers and other products have also begun to use UV-C technology to disinfect and sterilize air and water and ensure the health and hygiene of the family environment.
We Fiver Electronic Technology is a manufacturer of UV lamps for differenet types to meet different application scenarios needs, quality guarantee, cost effective. Please contact us for more infomation.
Post time:2024-12-26
